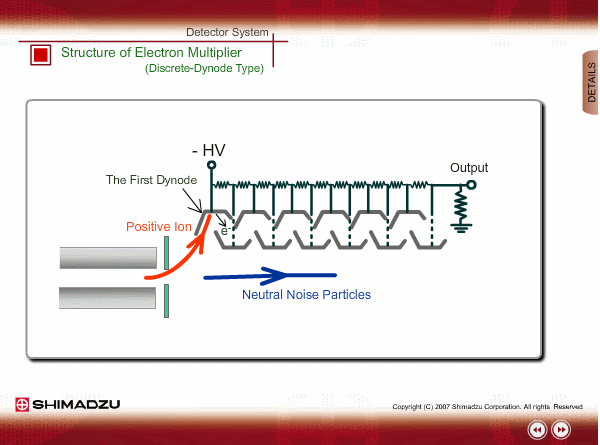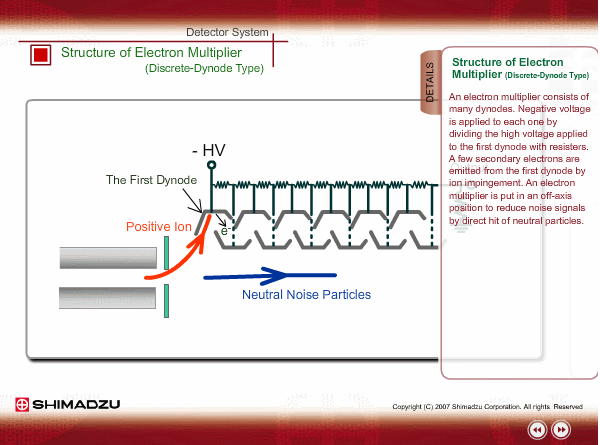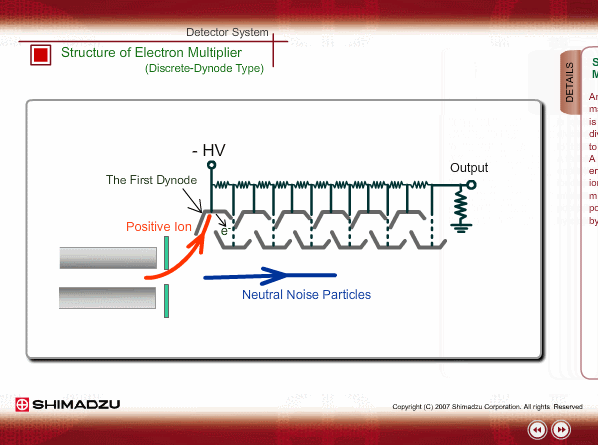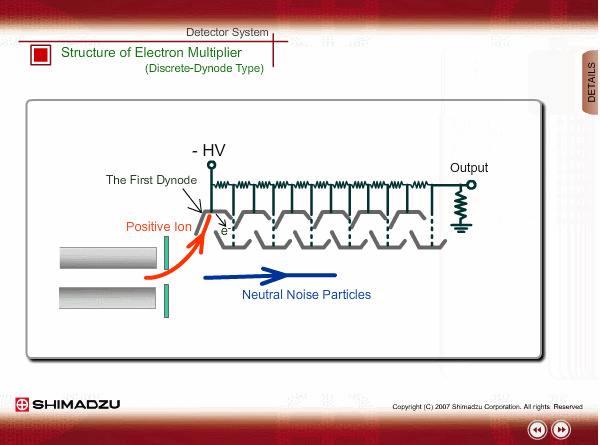
Structure of Electron Multiplier (Discrete-Dynode Type)
An electron multiplier consists of many dynodes. Negative voltage is applied to each one by dividing the high voltage applied to the first dynode with resisters. A few secondary electrons are emitted from the first dynode by ion impingement. An electron multiplier is put in an off-axis position to reduce noise signals by direct hit of neutral particles.
Next >> Electron Multiplication


